Studies found that more than 530,000 people had died worldwide from 15,000 extreme weather events in the last two decades, including floods, mudslides and droughts, with economic losses of $2.17 trillionThe report showed countries that are recurrently affected by catastrophes, such as the Philippines and Pakistan, and are included both in the long-term index and in the last 4 years' lists of countries most affected.
The year's strongest typhoon, Typhoon Rammasun (local name Glenda), killed around 100 people, destroyed over 100,000 houses and damaged 400,000 others.Philippine government data shows that more than 6,000 people were killed and millions of others were affected by super typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda) in 2013."Constant calamities from storms and floods take a heavy toll on the Philippines," said Raymund Liboro, assistant secretary for Climate Change and Disaster Risk Reduction of the Department of Science and Technology. "We realized that climate change is the defining challenge for our people and planet."
http://www.scientificamerican.com/article/philippines-hardest-hit-by-extreme-weather-in-2013/http://interaksyon.com/article/121069/philippines-included-in-top-of-climate-change-risk-list
Geology 9
Sunday, April 17, 2016
Thursday, April 7, 2016
Subsidence Hazards in the Philippines
According to the article, "Overpopulated..." by Rouchelle R. Dinglasan, a professor at the University of Illinois, Kelvin S. Rodolfo, has claimed that Metro Manila, the most populated city and the national capital region of the Philippines, is sinking faster than others may think due to overpopulation. Overpopulation results in over-pumping groundwater, over-pumping groundwater results in land subsidence, This subsidence is adding to the already rising water caused by global warming. Such land subsidence can create high tides that can reach farther into the land which can result in flooding. Citizens of the Philippines and geologists are coming together to find that the solution to this problem can only be reducing ground usage which means controlling population or bringing water from outside sources. Scientists are suggesting that big companies, houses, and fish pond owners to stop using groundwater to prevent such subsidence.

Any large, rapidly growing community built on a coastal river delta that uses much groundwater (is a candidate for rapid subsidence) - See more at: http://www.gmanetwork.com/news/story/298939/scitech/science/overpopulated-metro-manila-is-sinking-and-flooding-fast#sthash.MX1RLrKb.dpuf
Any large, rapidly growing community built on a coastal river delta that uses much groundwater (is a candidate for rapid subsidence) - See more at: http://www.gmanetwork.com/news/story/298939/scitech/science/overpopulated-metro-manila-is-sinking-and-flooding-fast#sthash.MX1RLrKb.dpuf
Friday, March 25, 2016
Mass Wasting Hazards in The Philippines
Back in 1999, on August 3, a huge landslide hit Antipolo City tin the Philippines due to a lot of heavy rain approaching the typhoon Olga. This landslide caused a lot of damage and loss of life, it became a death trap when the foundations were filled with water and the whole complex slid down hills. The Philippines began to alert citizens and residents were told to evacuate to the nearest town once the walls of their houses began to crack. They observe and look out for sudden changes in elevation and ground movements to try and prevent citizens from being hurt. Local authorities had warned residents to evacuate hours before the hazard occurred when cracks started to appear on the roads and walls, however, houses higher up on the hill began to slide down and crush those below.
 In November of 2006, Typhoon Reming hit the Philippines causing many lives lost when mudflows from the Mayon Volcano buried multiple villages due to strong winds and heavy rains. Typhoon Reming killed almost 2,000 people, and left hundreds of more people missing.
In November of 2006, Typhoon Reming hit the Philippines causing many lives lost when mudflows from the Mayon Volcano buried multiple villages due to strong winds and heavy rains. Typhoon Reming killed almost 2,000 people, and left hundreds of more people missing.Unfortunately, you cannot prevent such a hazard. Therefore, the Philippines could only prepare for what was coming. The government made sure various tropical cyclone warnings were shown and made sure the public was well aware it was coming. Officials made sure residents living in low areas seeked higher grounds, schools closed, and multiple buildings opened up storm shelters. Emergency shelters were available for those who left their homes.

On February 17, 2006, a huge rock slide and debris avalanche happened in the Philippines leaving over 1,000 people dead. This landslide was followed by 10 days straight of heavy rain and a minor earthquake. Burying a village and an elementary school affecting over 200 students and teachers.
http://landslides.usgs.gov/learn/photos/international/2006_guinsaugon_village__leyte_island_philippines_landslide
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Landslide
https://www.wsws.org/en/articles/1999/09/phil-s08.html
Thursday, February 18, 2016
Seismicity of The Philippines
Earthquakes are formed when the plates underneath the Earth’s surface move in different directions. These plates form a friction between each other in faults. It then sends a signal on an outward direction commonly known as seismic waves.
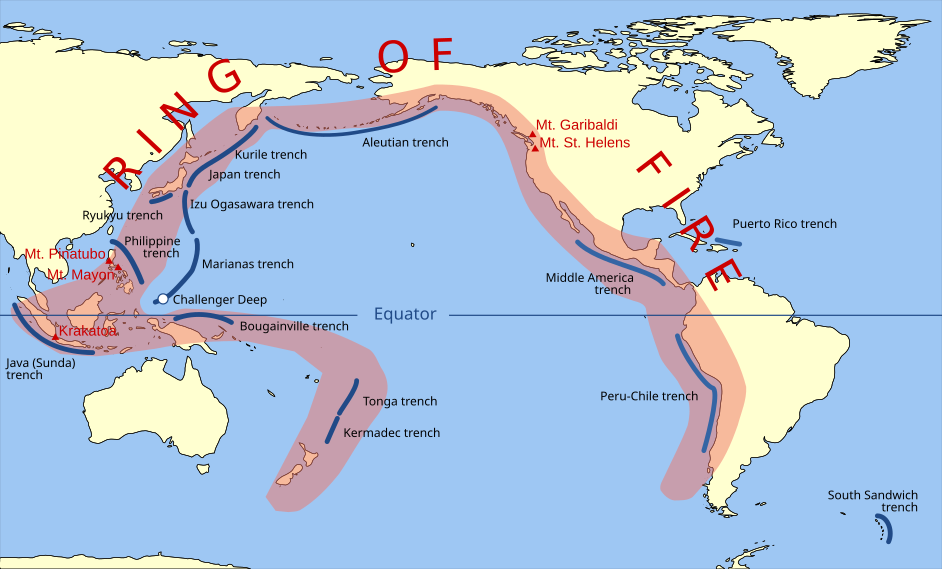
The Philippines lies along The Pacific Ring of Fire which causes lots of seismic waves and volcanic activity to happen in the country. Major tectonic plates meet in this region which causes a large number of earthquakes to happen. The Ring of Fire is an area in the Pacific Ocean where a large number of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions happen. It is horseshoe shape and associated with many oceanic trenches, volcanic arcs, and volcanic belts. It is sometimes referred to as the circum-pacific belt. About 90% of the world's earthquakes happen in The Ring of Fire.
According to officials, there isn't much The Philippines can do. They must improve emergency training and enforce building codes and make sure money is going in the right places to help those whose homes are the most vulnerable. However since The Philippines consists of small islands and is located on The Ring of Fire which is a main alleyway for typhoons, The Philippines will never be disaster proof.
https://www.washingtonpost.com/world/asia_pacific/in-the-philippines-natural-disasters-are-common-ways-to-reduce-impact-arent/2013/11/16/c0d77e24-4ecd-11e3-97f6-ed8e3053083b_story.html
Friday, February 12, 2016
Tectonic Plates
The Philippines is a part of the Eurasian Plate. The Eurasian plate consists of convergent boundaries. In a convergent boundary, tectonic plates move towards one another and collide in an active deforming area. Because of the pressure, friction, and plate material melting in the mantle, many earthquakes and volcanoes are common near convergent boundaries. In this destructive plate boundary, the subducting plate moves beneath the other plate. The subducting plate is usually a plate that contains oceanic crust and the other plate is usually made up of continental crust or oceanic crust as well.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Convergent_boundary
Thursday, February 4, 2016
Hazards, Disasters, Catastrophes
This picture is of a disaster that happened in Samar Island, an island of the Philippines.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)